Раздел: Документация
0 ... 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ... 20 is present. The rationale statements provide further support to the claim that such undesired behaviour is absent. 4.3.4toe summary specification The TOE summary specification provided in the ST defines the instantiation of the security requirements for the TOE. It provides a high-level definition of the security functions claimed to meet the functional requirements, and assurance measures taken to meet the assurance requirements. 4.3.5toe implementation The TOE implementation is the realisation of the TOE based on its security functional requirements and the TOE summary specification contained in the ST. TOE implementation is accomplished using a process of applying security and IT engineering skills and knowledge. The TOE will meet the security objectives if it correctly and effectively implements all the security requirements contained in the ST. 4.4 CC descriptive material The CC presents the framework in which an evaluation can take place. By presenting the requirements for evidence and analysis, a more objective, and hence useful evaluation result can be achieved. The CC incorporates a common set of constructs and a language in which to express and communicate the relevant aspects of IT security, and permits those responsible for IT security to benefit from the prior experience and expertise of others. 4.4.1 expression of security requirements The CC defines a set of constructs that combine into meaningful assemblies of security requirements of known validity, which can be used in establishing security requirements for prospective products and systems. The relationships among the various constructs for requirements expression are described below and illustrated in figure 4.6. 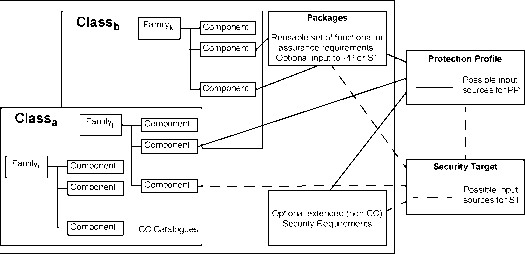 Figure 4.6 - Organisation and construction of requirements The organisation of the CC security requirements into the hierarchy of class - family - component is provided to help consumers to locate specific security requirements. The CC presents requirements for functional and assurance aspects in the same general style and uses the same organisation and terminology for each. 4.4.1.1Class The term class is used for the most general grouping of security requirements. All the members of a class share a common focus, while differing in coverage of security objectives. The members of a class are termed families. 4.4.1.2Family A family is a grouping of sets of security requirements that share security objectives but may differ in emphasis or rigour. The members of a family are termed components. 4.4.1.3Component A component describes a specific set of security requirements and is the smallest selectable set of security requirements for inclusion in the structures defined in the CC. The set of components within a family may be ordered to represent increasing strength or capability of security requirements that share a common purpose. They may also be partially ordered to represent related non-hierarchical sets. In some instances, there is only one component in a family so ordering is not applicable. The components are constructed from individual elements. The element is the lowest level expression of security requirements, and is the indivisible security requirement that can be verified by the evaluation. Dependencies between components Dependencies may exist between components. Dependencies arise when a component is not self sufficient and relies upon the presence of another component. Dependencies may exist between functional components, between assurance components, and between functional and assurance components. Component dependency descriptions are part of the CC component definitions. In order to ensure completeness of the TOE requirements, dependencies should be satisfied when incorporating components into PPs and STs where appropriate. Permitted operations on components CC components may be used exactly as defined in the CC, or they may be tailored through the use of permitted operations in order to meet a specific security policy or counter a specific threat. Each CC component identifies and defines any permitted operations of assignment and selection, the circumstances under which these operations may be applied to the component, and the results of the application of the operation. The operations of iteration and refinement can be performed for any component. These four operations are described as follows: a)iteration, which permits the use of a component more than once with varying operations; b)assignment, which permits the specification of a parameter to be filled in when the component is used; c)selection, which permits the specification of items that are to be selected from a list given in the component; d)refinement, which permits the addition of extra detail when the component is used. Some required operations may be completed (in whole or part) in the PP or may be left to be completed in the ST. Nevertheless, all operations must be completed in the ST. 4.4.2 use of security requirements The CC defines three types of requirement constructs: package, PP and ST. The CC further defines a set of IT security criteria that can address the needs of many communities and thus serve as a major expert input to the production of these constructs. The CC has been developed around the central notion of using wherever possible the security requirements components defined in the CC, which represent a well-known and understood domain. Figure 4.7 shows the relationship between these different constructs. 0 ... 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ... 20 |












